In this article, we will continue our learning about implementing relationships between entities in Spring Boot JPA. Today we will learn about implementing One-to-Many relationship.
One-to-Many Relationship
A one-to-many relationship is a type of cardinality that refers to the relationship between two entities A and B in which an element of A may be linked to many elements of B, but a member of B is linked to only one element of A.
Let's take an example of person and credit card, a person may have more than one credit card but one credit card is linked with only one person.
The person and passport classes are using Lombok to reduce boilerplate code, I suggest you to go through Lombok article .
Person.java
@Entity
@Table(name = "person")
@Getter @Setter @Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Person {
@Id
@Column(name = "person_id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Integer personId;
@Column(name = "person_name")
private String personName;
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL, fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
@JoinTable(name = "person_card_mapping",
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "person_id"),
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "card_id"))
private List<Card> cards;
}
Card.java
@Entity
@Table(name = "card")
@Getter @Setter @Builder
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Card {
@Id
@Column(name = "card_id")
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Integer cardId;
@Column(name = "card_no")
private String cardNo;
@Column(name = "cardholder_name")
private String cardholderName;
@Column(name = "expiry_month")
private String expiryMonth;
@Column(name = "expiry_year")
private String expiryYear;
}
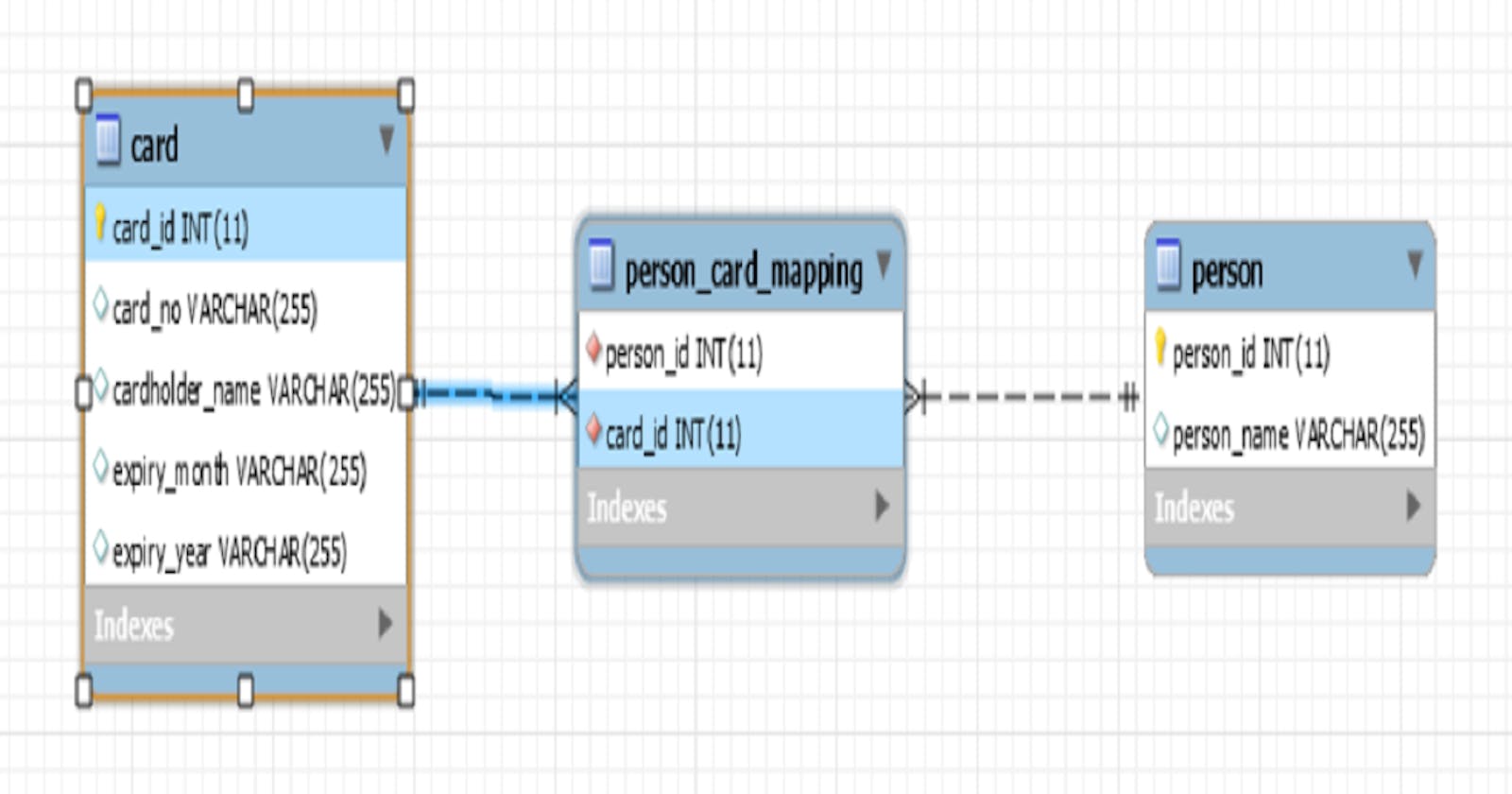
The relationship in the ER diagram is represented as follow:
The mapping is implemented in database using a mapping table which stores the primary key or identifying column from both the entities.
@JoinTable is used to specify the name of mapping table and joining column details.
name = "person_card_mapping" specifies the mapping table name where the primary keys will be stored.
joinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "person_id") specifies that from person table person_id column will be used to implement mapping.
inverseJoinColumns = @JoinColumn(name = "card_id")) specifies that from card table card_id column will be used to implement mapping.
Testing
Let's see a test case to test the unidirectional one-to-many relationship between Person and Cards.
@SpringBootTest
@TestInstance(TestInstance.Lifecycle.PER_CLASS)
public class OneToManyMappingTests {
@Autowired
private PersonRepository personRepo;
private Person person = null;
private Card card1 = null;
private Card card2 = null;
private Integer personId;
@BeforeAll
public void setup() {
card1 = Card.builder()
.cardholderName("John Doe")
.cardNo("4578963214502354")
.expiryMonth("12")
.expiryYear("2022")
.build();
card2 = Card.builder()
.cardholderName("John Doe")
.cardNo("4111111111111111")
.expiryMonth("02")
.expiryYear("2025")
.build();
List<Card> cards = new ArrayList<>();
cards.add(card1);
cards.add(card2);
person = Person.builder()
.personName("John Doe")
.cards(cards)
.build();
person = personRepo.save(person);
personId = person.getPersonId();
}
@Test
public void testOneToMany() {
Person person = personRepo.findById(personId).orElse(null);
assertNotNull(person.getCards());
assertEquals("4578963214502354", person.getCards().get(0).getCardNo());
assertEquals("4111111111111111", person.getCards().get(1).getCardNo());
}
}
On running this test case, we will find all these test cases runs successfully and verifies that our implementation is correct.
Summary
In this article, we learnt about implementation of one-to-many mapping relationship in Spring Data JPA. The other mapping relationship in Spring Data JPA will be discussed in further post.
Check this article for implementing One-to-One mapping.
Check this article for implementing Many-to-Many mapping.
You can find the source code of this post @ Github